Learning about Lexicons
Building on the last post I’ve been reminding myself what a lexicon is and how they are used in areas other than a compiler…
definition of lexicon
Definitions from Oxford Languages
noun: lexicon; plural noun: lexicons
- the vocabulary of a person, language, or branch of knowledge.
- a dictionary, especially of Greek, Hebrew, Syriac, or Arabic.
Linguistics
- the complete set of meaningful units in a language.
lexicons in the wild
ATProtocol
Lexicon is a schema definition language used to describe atproto records, HTTP endpoints (XRPC), and event stream messages. It builds on top of the atproto Data Model.
Take from their documentation
Bluesky
Paul Frazee is a software engineer at Bluesky, he’s posted Guidance on Authoring Lexicons
What is Lexicon? Lexicon is a schema definition tool. It establishes what data is expected in records or in RPC requests in the Atmosphere.
Every lexicon has an owner, which is established by its ID. The app.bsky.feed.post schema is controlled by whoever holds the feed.bsky.app domain name.
In general, it’s wise not to break that schema. You can, but other programs may discard your data.
Lexical Analysis
From the article on Wikipedia in Lexical Analysis
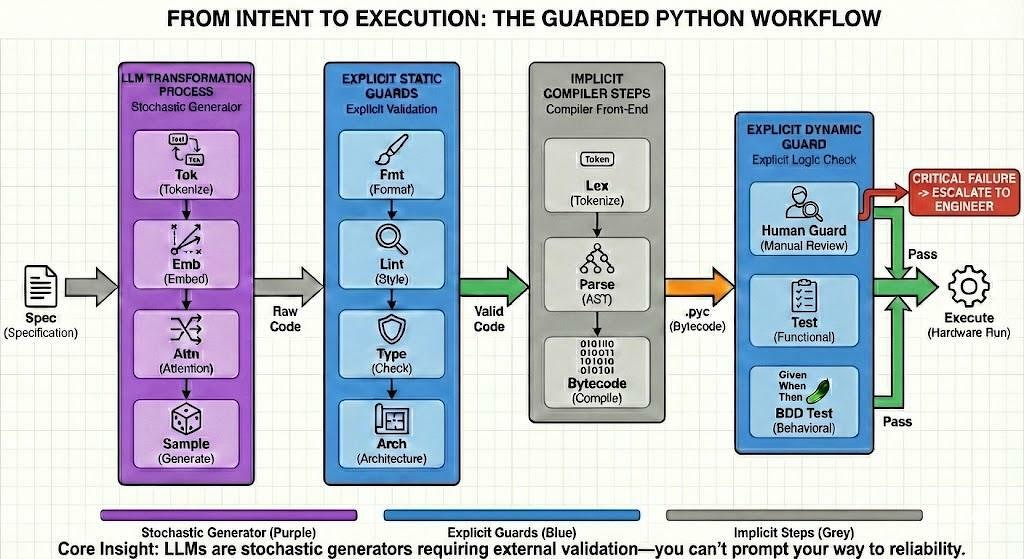
Lexical tokenization is conversion of a text into (semantically or syntactically) meaningful lexical tokens belonging to categories defined by a “lexer” program. In case of a natural language, those categories include nouns, verbs, adjectives, punctuations etc. In case of a programming language, the categories include identifiers, operators, grouping symbols, data types and language keywords. Lexical tokenization is related to the type of tokenization used in large language models (LLMs) but with two differences. First, lexical tokenization is usually based on a lexical grammar, whereas LLM tokenizers are usually probability-based. Second, LLM tokenizers perform a second step that converts the tokens into numerical values.
Which is a nice framing of the current state and how guards (like the AtomicGuard) can bridge gaps between probabilistic Lexical analysis of LLMs to the rules-based Lexical analysis of Compiler’s/Interpreters.